Purpose of This Guidance
Date of current publication: April 29, 2022
Lead authors: Shauna H. Gunaratne, MD, MPH, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY; Mary Beth Hansen, MA, Johns Hopkins University Clinical Guidelines Program, Baltimore, MD
Writing group: Joseph P. McGowan, MD, FACP, FIDSA; Steven M. Fine, MD, PhD; Rona Vail, MD; Samuel T. Merrick, MD; Asa Radix, MD, MPH, PhD; Charles J. Gonzalez, MD; Christopher J. Hoffmann, MD, MPH
Committee: Medical Care Criteria Committee
Date of original publication: April 29, 2022
This Committee encourages clinicians to adopt a patient-centered approach to sexual health care to improve the health and well-being of people in New York State (NYS) who receive HIV prevention and care services and prevention and care services related to other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
In a February 2020 Dear Colleague letter, the Director of the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) AIDS Institute (AI) noted that the prevailing disease-based approach to sexual health care is outdated and agreed with the American Sexual Health Association definition of sexual health: “the ability to embrace and enjoy our sexuality throughout our lives.” The letter explained that a sexual health framework:
“. . . includes ensuring that all people in NYS are empowered to exercise and achieve control over their sexual health and can access sexual health services that promote wellness in a manner that is respectful of their needs. This framework acknowledges sexuality as a life-long endeavor for people of all identities. It recognizes the importance of sexual pleasure, satisfaction, and intimacy to overall health and well-being.”
Adopting a patient-centered sexual health framework when implementing Clinical Guidelines Program recommendations and guidance for clinical care of people with HIV and other STIs can improve patients’ overall health and well-being, reduce stigma, empower patients, and increase their uptake of sexual health–related resources. The patient-centered, HIV status–neutral approach to sexual health encouraged here promotes disease prevention and harm reduction and recognizes that there is much more to sexual health than disease prevention and treatment.
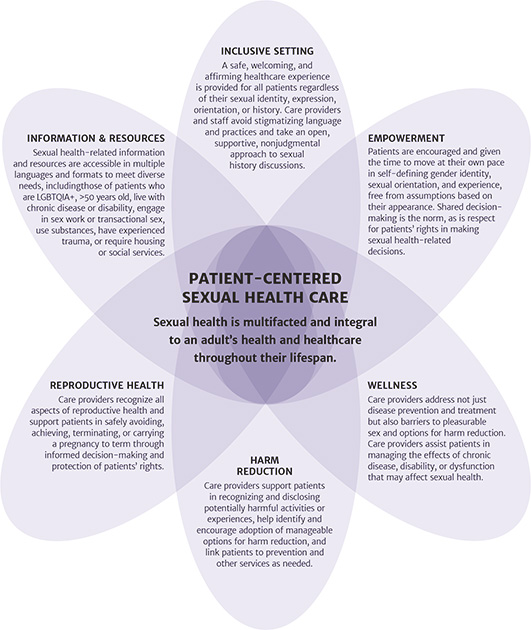
An individual’s sexual health may be related to their gender identity, sexual orientation, sexual practices, reproductive health and rights, safety, knowledge of harm reduction, disease prevention and treatment, and overall health. The multifaceted patient-centered sexual health framework illustrated in the figure below relies on open discussion of sexual identity, expression, experiences, preferences, and care planning and delivery. Sexual health is an important component of overall health that care providers should address as part of routine health visits.
Multifaceted Patient-Centered Sexual Health Care
Resources for Care Providers, below, provides links to a wide variety of informational sources that address the many facets of sexual health care.
Inclusive setting: All patients are entitled to a safe, welcoming, and affirming healthcare experience regardless of their sexual identity, expression, orientation, or experience. In an inclusive setting, care providers approach discussions of sexual health and history in an open and nonjudgmental manner and:
- Meet patients’ sexual health care needs regardless of gender, gender expression, sexual orientation, and sexual experience
- Recognize and respect that a patient’s gender identity, gender expression, sexual orientation, and sexual experience may not align with the care provider’s interpretation and understanding of each, may be fluid, and are defined by individual patients
- Focus on issues relevant to a patient’s care and does not rely on patients to satisfy others’ personal curiosity or to ensure that care providers or staff are comfortable with a patient’s gender identity, gender expression, and sexual experiences
- Avoid using stigmatizing language, such as “safe sex” or “high-risk sex,” when referring to patients’ experiences and maintain knowledge of up-to-date, accepted terminology
- Take an HIV status–neutral approach to discussions of sexual health
- Address structural, racial, socioeconomic, and cultural barriers to sexual health and health care
Empowerment: Care providers and staff refrain from making any assumptions based on a patient’s age, physical appearance, or gender expression and:
- Ask patients to identify their preferred pronouns and then ensure use of these pronouns when addressing patients
- Support patients in identifying their sexual identity, orientation, experience, and needs
- Engage patients in shared decision-making for care planning
- Support patients in setting the pace in discussions of sexual experience with their care providers and sexual partners
- Support and encourage patients’ self-efficacy
- Provide information that can help reduce stigma and fear, such as information about U=U (undetectable = untransmittable) for patients with HIV
- Advocate for patients’ sexual rights, including the right to make sexual health–related decisions
Wellness: Recognizing that sexual health depends on more than just disease prevention or treatment and taking a comprehensive approach to sexual health care, care providers:
- Ask about patients’ comfort with sex or pain during sex and assist patients in overcoming challenges, including those posed by age-related physiologic changes, chronic disease, disability, or dysfunction
- Recognize that the concerns of patients ≥50 years old may differ from those of younger patients
- Recognize that patients’ sexual health concerns may change as they age and avoid assumptions based on a patient’s age
- Screen for erectile dysfunction in patients who may be at risk
- Educate patients about the possible sexual health effects of chronic conditions
- Provide information and support for patients to achieve intimacy and sexual satisfaction
Harm reduction: To identify and meet patients’ needs for harm reduction counseling and education, care providers:
- Encourage patients to disclose experiences that may be harmful, including activities that may lead to acquisition of STIs, such as condomless sex, drug use, and sex with multiple or anonymous partners
- Ask patients if they engage in transactional sex and link to services as needed
- Ask open-ended questions about any experience with sexual violence, intimate partner violence, or other types of abuse and link patients to services as needed
- Educate patients about harm reduction and help them identify and implement manageable options
- Ensure that patients who do not have HIV know about pre- and post-exposure prophylaxis and about how to access both
Reproductive health: Recognizing that reproductive health and services are central to sexual health for many patients, care providers:
- Provide information about contraceptive choices for all genders
- Link patients to gynecologic and obstetric care, abortion services, and other services as needed
- Educate patients with HIV who wish to conceive with a serodifferent partner about U=U
Information and resources: Sexual health–related information and resources are readily available in multiple languages and formats to meet diverse needs, including those of patients who:
- Identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, questioning, queer, intersex, asexual, pansexual, or gender fluid (LGBTQIA+)
- Are ≥50 years old
- Live with chronic disease or disability
- Engage in transactional sex or sex work
- Use substances
- Have experienced trauma
- Require housing, social services, or other specialized services
- Have low or no literacy or health literacy
- Have limited or no computer or internet access
- Require or prefer receiving information via audio or video
Components of a Patient-Centered Approach
Figure 1: Components of a Patient-Centered Approach to Sexual Health Care
Download figure: Components of a Patient-Centered Approach to Sexual Health Care
Resources for Care Providers
NYSDOH:
- Comprehensive Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care Services Program
- GOALS Framework for Sexual History Taking in Primary Care
- Older Adults and Sexual Health: A Guide for Aging Services Providers
- PrEP to Prevent HIV and Promote Sexual Health
- Sexual Violence Prevention Program
- STI self-collection outside of a clinic setting in NYS Question & Answer
- Women’s Health
- U=U Guidance for Implementation in Clinical Settings
American Academy of HIV Medicine: Sexual Health in HIV and Aging Clinical Recommendations
American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT): https://www.aasect.org/
American Sexual Health Association (ASHA):
Better Health Channel: Sex and Chronic Illness
Canadian Public Health Association: Discussing Sexual Health, Substance Use and STBBIs (sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
Gay & Lesbian Medical Association: Guidelines for Care of Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Patients
HIV.gov: Standing Up to Stigma
International Society of Sexual Medicine (ISSM): https://www.issm.info/
National Association of County & City Health Officials: Including People With Disabilities in Reproductive Health Programs and Services
National Coalition for Sexual Health:
- A New Approach to Sexual History Taking: Talking About Pleasure, Problems, and Pride During a Sexual History (videos)
- Sexual Health and Your Patients: A Provider’s Guide
National Institute on Aging: Sexuality and Intimacy in Older Adults
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center:
- Glossary of Terms for Health Care Teams
- Learning Resources—Reproductive Health
- Sexual Health Care for Older LGBTQIA+ Adults (2021)
- Stigma Resources
- Ten Strategies for Creating Inclusive Health Care Environments for LGBTQIA+ People (2021)
New York City Health: Sexual and Reproductive Justice
Positive Women’s Network: Harm Reduction Factsheet
Reproductive Health Access Project: Focus on Abortion, Contraception, Miscarriage
Reproductive Health National Training Center: Patient Experience Improvement Toolkit
Sexual Medicine Society of North America (SMSNA): https://www.smsna.org
The Well Project: Undetectable Equals Untransmittable: Building Hope and Ending HIV Stigma
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS: Transactional Sex and HIV Risk: From Analysis to Action
Shared Decision-Making
Download Printable PDF of Shared Decision-Making Statement
Date of current publication: August 8, 2023
Lead authors: Jessica Rodrigues, MS; Jessica M. Atrio, MD, MSc; and Johanna L. Gribble, MA
Writing group: Steven M. Fine, MD, PhD; Rona M. Vail, MD; Samuel T. Merrick, MD; Asa E. Radix, MD, MPH, PhD; Christopher J. Hoffmann, MD, MPH; Charles J. Gonzalez, MD
Committee: Medical Care Criteria Committee
Date of original publication: August 8, 2023
Rationale
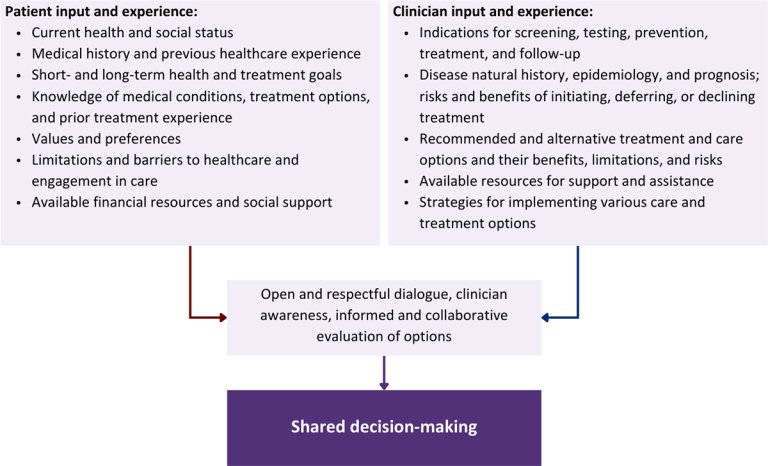
Throughout its guidelines, the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) AIDS Institute (AI) Clinical Guidelines Program recommends “shared decision-making,” an individualized process central to patient-centered care. With shared decision-making, clinicians and patients engage in meaningful dialogue to arrive at an informed, collaborative decision about a patient’s health, care, and treatment planning. The approach to shared decision-making described here applies to recommendations included in all program guidelines. The included elements are drawn from a comprehensive review of multiple sources and similar attempts to define shared decision-making, including the Institute of Medicine’s original description [Institute of Medicine 2001]. For more information, a variety of informative resources and suggested readings are included at the end of the discussion.
Benefits
The benefits to patients that have been associated with a shared decision-making approach include:
- Decreased anxiety [Niburski, et al. 2020; Stalnikowicz and Brezis 2020]
- Increased trust in clinicians [Acree, et al. 2020; Groot, et al. 2020; Stalnikowicz and Brezis 2020]
- Improved engagement in preventive care [McNulty, et al. 2022; Scalia, et al. 2022; Bertakis and Azari 2011]
- Improved treatment adherence, clinical outcomes, and satisfaction with care [Crawford, et al. 2021; Bertakis and Azari 2011; Robinson, et al. 2008]
- Increased knowledge, confidence, empowerment, and self-efficacy [Chen, et al. 2021; Coronado-Vázquez, et al. 2020; Niburski, et al. 2020]
Approach
Collaborative care: Shared decision-making is an approach to healthcare delivery that respects a patient’s autonomy in responding to a clinician’s recommendations and facilitates dynamic, personalized, and collaborative care. Through this process, a clinician engages a patient in an open and respectful dialogue to elicit the patient’s knowledge, experience, healthcare goals, daily routine, lifestyle, support system, cultural and personal identity, and attitudes toward behavior, treatment, and risk. With this information and the clinician’s clinical expertise, the patient and clinician can collaborate to identify, evaluate, and choose from among available healthcare options [Coulter and Collins 2011]. This process emphasizes the importance of a patient’s values, preferences, needs, social context, and lived experience in evaluating the known benefits, risks, and limitations of a clinician’s recommendations for screening, prevention, treatment, and follow-up. As a result, shared decision-making also respects a patient’s autonomy, agency, and capacity in defining and managing their healthcare goals. Building a clinician-patient relationship rooted in shared decision-making can help clinicians engage in productive discussions with patients whose decisions may not align with optimal health outcomes. Fostering open and honest dialogue to understand a patient’s motivations while suspending judgment to reduce harm and explore alternatives is particularly vital when a patient chooses to engage in practices that may exacerbate or complicate health conditions [Halperin, et al. 2007].
Options: Implicit in the shared decision-making process is the recognition that the “right” healthcare decisions are those made by informed patients and clinicians working toward patient-centered and defined healthcare goals. When multiple options are available, shared decision-making encourages thoughtful discussion of the potential benefits and potential harms of all options, which may include doing nothing or waiting. This approach also acknowledges that efficacy may not be the most important factor in a patient’s preferences and choices [Sewell, et al. 2021].
Clinician awareness: The collaborative process of shared decision-making is enhanced by a clinician’s ability to demonstrate empathic interest in the patient, avoid stigmatizing language, employ cultural humility, recognize systemic barriers to equitable outcomes, and practice strategies of self-awareness and mitigation against implicit personal biases [Parish, et al. 2019].
Caveats: It is important for clinicians to recognize and be sensitive to the inherent power and influence they maintain throughout their interactions with patients. A clinician’s identity and community affiliations may influence their ability to navigate the shared decision-making process and develop a therapeutic alliance with the patient and may affect the treatment plan [KFF 2023; Greenwood, et al. 2020]. Furthermore, institutional policy and regional legislation, such as requirements for parental consent for gender-affirming care for transgender people or insurance coverage for sexual health care, may infringe upon a patient’s ability to access preventive- or treatment-related care [Sewell, et al. 2021].
Figure 1: Elements of Shared Decision-Making
Download figure: Elements of Shared Decision-Making
Health equity: Adapting a shared decision-making approach that supports diverse populations is necessary to achieve more equitable and inclusive health outcomes [Castaneda-Guarderas, et al. 2016]. For instance, clinicians may need to incorporate cultural- and community-specific considerations into discussions with women, gender-diverse individuals, and young people concerning their sexual behaviors, fertility intentions, and pregnancy or lactation status. Shared decision-making offers an opportunity to build trust among marginalized and disenfranchised communities by validating their symptoms, values, and lived experience. Furthermore, it can allow for improved consistency in patient screening and assessment of prevention options and treatment plans, which can reduce the influence of social constructs and implicit bias [Castaneda-Guarderas, et al. 2016].
Clinician bias has been associated with health disparities and can have profoundly negative effects [FitzGerald and Hurst 2017; Hall, et al. 2015]. It is often challenging for clinicians to recognize and set aside personal biases and to address biases with peers and colleagues. Consciously or unconsciously, negative or stigmatizing assumptions are often made about patient characteristics, such as race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, mental health, and substance use [Avery, et al. 2019; van Boekel, et al. 2013; Livingston, et al. 2012]. With its emphasis on eliciting patient information, a shared decision-making approach encourages clinicians to inquire about patients’ lived experiences rather than making assumptions and to recognize the influence of that experience in healthcare decision-making.
Stigma: Stigma may prevent individuals from seeking or receiving treatment and harm reduction services [Tsai, et al. 2019]. Among people with HIV, stigma and medical mistrust remain significant barriers to healthcare utilization, HIV diagnosis, and medication adherence and can affect disease outcomes [Turan, et al. 2017; Chambers, et al. 2015], and stigma among clinicians against people who use substances has been well-documented [Stone, et al. 2021; Tsai, et al. 2019; van Boekel, et al. 2013]. Sexual and reproductive health, including strategies to prevent HIV transmission, acquisition, and progression, may be subject to stigma, bias, social influence, and violence.
| SHARED DECISION-MAKING IN HIV CARE |
|
Resources and Suggested Reading
In addition to the references cited below, the following resources and suggested reading may be useful to clinicians.
| RESOURCES |
References
Acree ME, McNulty M, Blocker O, et al. Shared decision-making around anal cancer screening among black bisexual and gay men in the USA. Cult Health Sex 2020;22(2):201-16. [PMID: 30931831]
Avery JD, Taylor KE, Kast KA, et al. Attitudes toward individuals with mental illness and substance use disorders among resident physicians. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2019;21(1):18m02382. [PMID: 30620451]
Bertakis KD, Azari R. Patient-centered care is associated with decreased health care utilization. J Am Board Fam Med 2011;24(3):229-39. [PMID: 21551394]
Castaneda-Guarderas A, Glassberg J, Grudzen CR, et al. Shared decision making with vulnerable populations in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 2016;23(12):1410-16. [PMID: 27860022]
Chambers LA, Rueda S, Baker DN, et al. Stigma, HIV and health: a qualitative synthesis. BMC Public Health 2015;15:848. [PMID: 26334626]
Chen CH, Kang YN, Chiu PY, et al. Effectiveness of shared decision-making intervention in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases: a randomized controlled trial. Patient Educ Couns 2021;104(10):2498-2504. [PMID: 33741234]
Coronado-Vázquez V, Canet-Fajas C, Delgado-Marroquín MT, et al. Interventions to facilitate shared decision-making using decision aids with patients in primary health care: a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99(32):e21389. [PMID: 32769870]
Coulter A, Collins A. Making shared decision-making a reality: no decision about me, without me. 2011. https://www.kingsfund.org.uk/sites/default/files/Making-shared-decision-making-a-reality-paper-Angela-Coulter-Alf-Collins-July-2011_0.pdf
Crawford J, Petrie K, Harvey SB. Shared decision-making and the implementation of treatment recommendations for depression. Patient Educ Couns 2021;104(8):2119-21. [PMID: 33563500]
FitzGerald C, Hurst S. Implicit bias in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. BMC Med Ethics 2017;18(1):19. [PMID: 28249596]
Greenwood BN, Hardeman RR, Huang L, et al. Physician-patient racial concordance and disparities in birthing mortality for newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020;117(35):21194-21200. [PMID: 32817561]
Groot G, Waldron T, Barreno L, et al. Trust and world view in shared decision making with indigenous patients: a realist synthesis. J Eval Clin Pract 2020;26(2):503-14. [PMID: 31750600]
Hall WJ, Chapman MV, Lee KM, et al. Implicit racial/ethnic bias among health care professionals and its influence on health care outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Public Health 2015;105(12):e60-76. [PMID: 26469668]
Halperin B, Melnychuk R, Downie J, et al. When is it permissible to dismiss a family who refuses vaccines? Legal, ethical and public health perspectives. Paediatr Child Health 2007;12(10):843-45. [PMID: 19043497]
Institute of Medicine. Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. 2001. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222274/
KFF. Key data on health and health care by race and ethnicity. 2023 Mar 15. https://www.kff.org/racial-equity-and-health-policy/report/key-data-on-health-and-health-care-by-race-and-ethnicity/ [accessed 2023 May 19]
Livingston JD, Milne T, Fang ML, et al. The effectiveness of interventions for reducing stigma related to substance use disorders: a systematic review. Addiction 2012;107(1):39-50. [PMID: 21815959]
McNulty MC, Acree ME, Kerman J, et al. Shared decision making for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with black transgender women. Cult Health Sex 2022;24(8):1033-46. [PMID: 33983866]
Niburski K, Guadagno E, Abbasgholizadeh-Rahimi S, et al. Shared decision making in surgery: a meta-analysis of existing literature. Patient 2020;13(6):667-81. [PMID: 32880820]
Parish SJ, Hahn SR, Goldstein SW, et al. The International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health process of care for the identification of sexual concerns and problems in women. Mayo Clin Proc 2019;94(5):842-56. [PMID: 30954288]
Robinson JH, Callister LC, Berry JA, et al. Patient-centered care and adherence: definitions and applications to improve outcomes. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 2008;20(12):600-607. [PMID: 19120591]
Scalia P, Durand MA, Elwyn G. Shared decision-making interventions: an overview and a meta-analysis of their impact on vaccine uptake. J Intern Med 2022;291(4):408-25. [PMID: 34700363]
Sewell WC, Solleveld P, Seidman D, et al. Patient-led decision-making for HIV preexposure prophylaxis. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2021;18(1):48-56. [PMID: 33417201]
Stalnikowicz R, Brezis M. Meaningful shared decision-making: complex process demanding cognitive and emotional skills. J Eval Clin Pract 2020;26(2):431-38. [PMID: 31989727]
Stone EM, Kennedy-Hendricks A, Barry CL, et al. The role of stigma in U.S. primary care physicians’ treatment of opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend 2021;221:108627. [PMID: 33621805]
Tsai AC, Kiang MV, Barnett ML, et al. Stigma as a fundamental hindrance to the United States opioid overdose crisis response. PLoS Med 2019;16(11):e1002969. [PMID: 31770387]
Turan B, Budhwani H, Fazeli PL, et al. How does stigma affect people living with HIV? The mediating roles of internalized and anticipated HIV stigma in the effects of perceived community stigma on health and psychosocial outcomes. AIDS Behav 2017;21(1):283-91. [PMID: 27272742]
van Boekel LC, Brouwers EP, van Weeghel J, et al. Stigma among health professionals towards patients with substance use disorders and its consequences for healthcare delivery: systematic review. Drug Alcohol Depend 2013;131(1-2):23-35. [PMID: 23490450]
Updates, Authorship, and Related Guidelines
| Updates, Authorship, and Related Guidelines | |
| Date of original publication | April 29, 2022 |
| Intended users | NYS clinicians |
| Lead author(s) |
Shauna H. Gunaratne, MD, MPH, Columbia University Irving Medical Center; Mary Beth Hansen, MA, Johns Hopkins University Clinical Guidelines Program |
| Writing group |
Joseph P. McGowan, MD, FACP, FIDSA; Steven M. Fine, MD, PhD; Rona Vail, MD; Samuel T. Merrick, MD; Asa Radix, MD, MPH, PhD; Charles J. Gonzalez, MD; Christopher J. Hoffmann, MD, MPH |
| Author and writing group conflict of interest disclosures | There are no author or writing group conflict of interest disclosures |
| Committee | |
| Developer and funder |
New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute (NYSDOH AI) |
| Development process |
See Guideline Development and Recommendation Ratings Scheme, below. |
| Related NYSDOH AI guidelines |
Related NYSDOH AI Guidance |
Guideline Development and Recommendation Ratings
| Guideline Development: New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute Clinical Guidelines Program | |
| Program manager | Clinical Guidelines Program, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. See Program Leadership and Staff. |
| Mission | To produce and disseminate evidence-based, state-of-the-art clinical practice guidelines that establish uniform standards of care for practitioners who provide prevention or treatment of HIV, viral hepatitis, other sexually transmitted infections, and substance use disorders for adults throughout New York State in the wide array of settings in which those services are delivered. |
| Expert committees | The NYSDOH AI Medical Director invites and appoints committees of clinical and public health experts from throughout New York State to ensure that the guidelines are practical, immediately applicable, and meet the needs of care providers and stakeholders in all major regions of New York State, all relevant clinical practice settings, key New York State agencies, and community service organizations. |
| Committee structure |
|
| Disclosure and management of conflicts of interest |
|
| Evidence collection and review |
|
| Recommendation development |
|
| Review and approval process |
|
| External reviews |
|
| Update process |
|
| Recommendation Ratings Scheme | |||
| Strength | Quality of Evidence | ||
| Rating | Definition | Rating | Definition |
| A | Strong | 1 | Based on published results of at least 1 randomized clinical trial with clinical outcomes or validated laboratory endpoints. |
| B | Moderate | * | Based on either a self-evident conclusion; conclusive, published, in vitro data; or well-established practice that cannot be tested because ethics would preclude a clinical trial. |
| C | Optional | 2 | Based on published results of at least 1 well-designed, nonrandomized clinical trial or observational cohort study with long-term clinical outcomes. |
| 2† | Extrapolated from published results of well-designed studies (including nonrandomized clinical trials) conducted in populations other than those specifically addressed by a recommendation. The source(s) of the extrapolated evidence and the rationale for the extrapolation are provided in the guideline text. One example would be results of studies conducted predominantly in a subpopulation (e.g., one gender) that the committee determines to be generalizable to the population under consideration in the guideline. | ||
| 3 | Based on committee expert opinion, with rationale provided in the guideline text. | ||
Last updated on October 23, 2023

